 |
 |
- Search
| Neurointervention > Volume 11(1); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
The aim is to provide evidence of the internationalization of Neurointervention based on journal metrics for articles published from 2011 to 2015.
Materials and Methods
The following metrics and data were collected and analyzed with descriptive statistics: number of citable and non-citable articles; number of research articles (original papers) supported by grants; editorial board members' countries; authors' countries; citing authors' countries; source title of citing articles; two-year impact factor; total citations; and Hirsch index (h-index). Data were retrieved and analyzed from the journal homepage and Web of Science Core Collection in January 24, 2016.
Results
There were 80 citable and eight non-citable articles from 2011 to 2015. Out of 31 original articles, nine had research funds (29.0%). Editorial board members are from five countries. The authors are from six countries. The top-ranking countries of citing authors were USA, Korea, and China. The two-year impact factors were 1.125, 0.923, and 0.931 from 2013 to 2015. H-index was 7.
After changing to an English language journal in February 2011, Neurointervention was rapidly and brilliantly promoted to an international journal. The reason why Neurointervention should be indexed in international databases was explained at that time [1]. From November 28, 2011, it began to be indexed in PubMed Central/PubMed. I would like to provide evidence of internationalization of the journal based on journal metrics from 2011 to 2015.
The following metrics and data were collected and analyzed with descriptive statistics: number of citable and non-citable articles; number of research articles (original papers) supported by grants; editorial board members' countries; authors' countries; citing authors' countries; source title of citing articles; two-year impact factor; total citations; and Hirsch index (h-index). Citable articles comprised publication types of original articles, technical notes, reviews, guidelines, study designs, and case reports. Analysis was based on the Web of Science Core Collection. Target articles were limited to articles in Neurointervention from 2011 to 2015; therefore, articles published before 2011 were not included in the analysis. Even though manual calculation of the two-year impact factor and h-index were already well described in previous articles [2], it can be briefly described as follows:
The 2015 two-year impact factor can be calculated as follows:
Number of citable articles published in Neurointervention in 2013: A
Number of citable articles published in Neurointervention in 2014: B
Citation number of Neurointervention articles published in 2013 by 2015 Web of Science articles: C
Citation number of Neurointervention articles published in 2014 by 2015 Web of Science articles: D
2015 two-year impact factor of Neurointervention = (C+D)/(A+B)
The h-index of a journal can be defined as follows. A journal has index h, if Np journal articles have at least h citations each and the other (Np-h) articles have equal to or less than h citations each (where Np defines this cutoff in an ordered ranking of journal articles by citation number). Counting and analysis of data was done January 24, 2016.
There were 80 citable and eight non-citable articles from 2011 to 2015 (Fig. 1). Out of 31 original articles, nine received research funds (29.0%) (Fig. 2). The number of editorial board members, according to country, was as follows: 12 from Korea, 2 each from China, Japan, and the USA, and 1 from Sweden. The number of articles according to authors' countries were as follows: 71 from Korea, 10 from the USA, and 4 from China, 3 each from Hong Kong and India, and 2 from Japan. Out of 88 articles from 2011 to 2015, 48 articles (54.5%) were cited at least one time in Web of Science. Citing authors' countries were traced in Fig. 3. The top ranking citing countries were USA (46), Korea (45), China (28), and Germany (13). Ninety titles cited Neurointervention (Fig. 4). The top ranking source titles were Journal of Korean Neurosugical Society (12), Interventional Neuroradiology (12), Stroke (9), Neurosurgery (9), Journal of Neurointerventional Surgery (9), and American Journal of Neuroradiology (9). Out of 90 citing journals, some are from Korea: Journal of Korean Neurosugical Society (12), Korean Journal of Radiology (4), Journal of Stroke (3), Korean Journal of Internal Medicine (1), and Journal of Clinical Neurology (1). Two-year impact factors were 1.125 in 2013, 0.923 in 2014, and 0.931 in 2015. The total citation increased year by year from 2 in 2011, 13 in 2012, 39 in 2013, 53 in 2014, and 65 in 2015. An h-index of 7 can be verified from Table 1. Out of eight highly cited articles, the publication type of six articles was an original article.
The above results showed that Neurointervention was promoted to an international journal based on journal metrics. The proportion of funded articles out of original articles, 29.0%, is comparable to other medical journals in Korea: Annals of rehabilitation Medicine, 34.2% [3]; Clinical Endoscopy, 38.2% [4]; Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine, 39.8% [5]; Diabetes & Metabolism Journal, 43.9% [6]; International Neurourology Journal, 38.6% [7]; and Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, 29.0% [8].
The number of editorial board members' countries, five, is not enough. More vigorous recruitment of editorial board members from more than 30 countries is required to recruit manuscripts from a variety of countries. Up to the last issue of 2015, only authors from six countries had published in Neurointervention. The expansion of the editorial board may be able to contribute to the expansion of authors' countries.
The fact that more than half of the articles in Neurointervention from 2011 to 2015 were cited by Web of Science Core Collection articles shows well-propagation through PubMed and PubMed Central. If local English journals are included in PubMed and PubMed Central, its impact factor would soar dramatically [9]. Maintenance of two-year impact factor and an increase in total citation year by year might be evidence of an effect of PubMed and PubMed Central. The year 2015 two-year impact factor of 0.931 corresponds to 106th (84.8%) out of 125 journals in the 2014 JCR category of radiology, nuclear medicine & medical imaging. The total citation in 2015 surpassed five times the citable article number published in 2015.
An h-index of 7 is a high value, because the number of citable articles published from 2011 to 2015 was just 80. The Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions had an h-index of 5, of which the number of citable articles from 2004 was 141, [8]. Original articles received a higher citation number than review articles. This is comparable to other journals: In Korean Journal of Urology, out of 15 highly-cited articles, the publication type of 12 was an original article [10]. In Archives of Plastic Surgery, there were three reviews, three original articles and one case report out of seven of the most highly-cited articles [11]. Out of 12 highly-cited articles of Korean Journal of Internal Medicine, there were four reviews and six original articles [12].
This wonderful promotion to the international level was possible from the editor's and board members' devotion, and from full support by the publisher, the Korean Society of Interventional Neuroradiology. Besides these efforts, the introduction of digital standards to the journal was essential for journal promotion. Journal article tag suite XML (formerly PubMed Central XML) [13,14] and digital object identifier [15] were core standards. Introduction of those services was essential to the dissemination of journal content to researchers and physicians worldwide. Furthermore, open researchers and contributors ID [16], QR code [17], and CrossRef text and data mining services [18] should be introduced soon for more rapid propagation of information and the disclosure of author information. Audio and video presentation of content also should be considered [19].
Analysis of metrics for Neurointervention showed that it has been already promoted to the international level. The year 2015 impact factor corresponds to 84.8% in the 2014 JCR radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging category. It was possible by introducing Journal Article Tag Suite XML and digital object identifier, which provide a way for dissemination to the world. For further promotion, editorial board members from at least 30 countries and authors from more than 20 countries should be recruited soon. Also, digital standards such as ORCID, QR code, CrossRef text and data mining, and audio-visual presentation should be considered for adoption.
References
1. Huh S. Why should Neurointervention be indexed in International Databases? Neurointervention 2011;6:49-50 .



2. Huh S. Citation Analysis of the Korean Journal of Urology From Web of Science, Scopus, Korean Medical Citation Index, KoreaMed Synapse, and Google Scholar. Korean J Urol 2013;54:220-228 .



3. Huh S. The Elevation of Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine to the Status of an International Journal After Adopting an English-Only Policy. Ann Rehabil Med 2015;39:661-666 .



4. Huh S. Evidence of the Internationalization of Clinical Endoscopy Based on Journal Metrics. Clin Endosc 2015;48:317-321 .



5. Huh S. What is the position of Clinical and Experimental Reproductive Medicine in its scholarly journal network based on journal metrics? Clin Exp Reprod Med 2014;41:147-150 .



6. Huh S. Journal metrics-based position of Diabetes & Metabolism Journal after the change of its text language to english. Diabetes Metab J 2014;38:187-193 .



7. Huh S. How far has the international neurourology journal progressed since its transformation into an english language journal? Int Neurourol J 2014;18:3-9 .



8. Huh S. How much is Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions promoted based on journal metrics? J Educ Eval Health Prof 2015;12:57.



9. Jeong GH, Huh S. Increase in frequency of citation by SCIE journals of non-Medline journals after listing in an open access full-text database. Sci Ed 2014;1:24-26.

10. Huh S. How much progress has been made in journal metrics two years after the citation analysis of the Korean Journal of Urology? Korean J Urol 2015;56:276-279 .



11. Huh S. How journal metrics illustrate the transformation of archives of plastic surgery into an international journal. Arch Plast Surg 2014;41:617-619 .



12. Huh S. How far has The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine advanced in terms of journal metrics? Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:635-638 .



13. Huh S. Journal Article Tag Suite 1.0: National Information Standards Organization standard of journal extensible markup language. Sci Ed 2014;1:99-104.

14. Huh S. Coding practice of the Journal Article Tag Suite extensible markup language. Sci Ed 2014;1:105-112.

Fig. 1
Number of citable and non-citable articles in Neurointervention from 2011 to 2015 [cited 2016 Jan 24].

Fig. 2
Number of funded and not-funded research articles in Neurointervention from 2011 to 2015 [cited 2016 Jan 24].
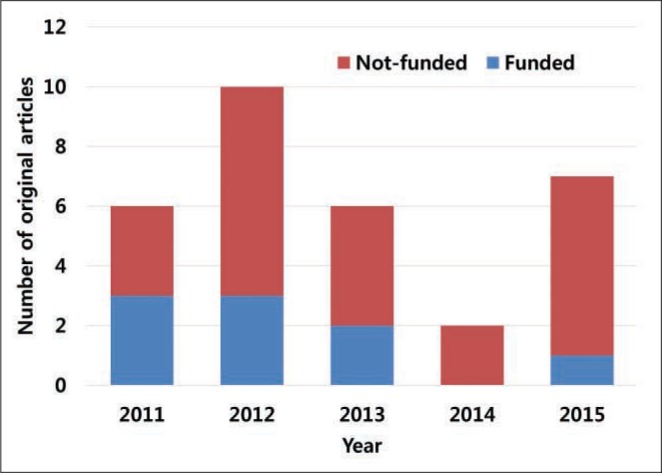
Fig. 3
Number of articles by country citing Neurointervention from Web of Science Core Collection from 2011 to 2015 [cited 2016 Jan 24].
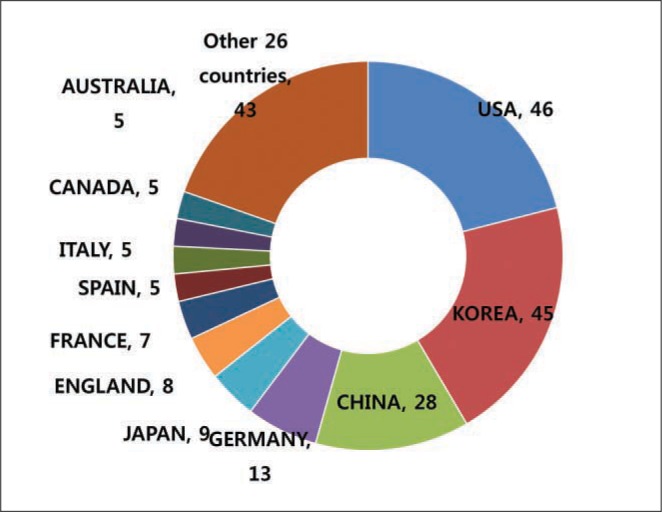
Fig. 4
Source titles of articles citing Neurointervention from Web of Science Core Collection from 2011 to 2015 [cited 2016 Jan 24].
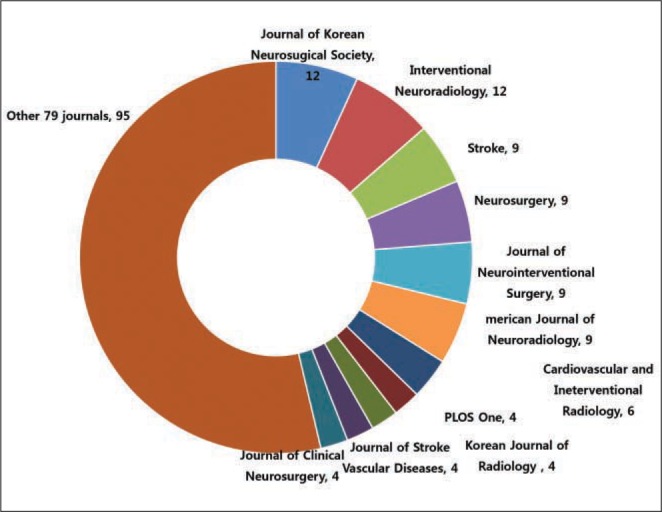
Table 1
Hirsch Index of Neurointervention was 7 Because at Least 7 Articles were Cited by Web of Science Articles at Least 7 Times Each
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 7 Crossref
- 4,693 View
- 63 Download
- Related articles in NI
-
Why should
Neurointervention be indexed in International Databases?2011 August;6(2)