 |
 |
- Search
| Neurointervention > Volume 13(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
For many years, the pathophysiology of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) was interpreted as ŌĆ£secondary intracranial hypertension,ŌĆØ and IIH was considered to be caused by brain edema due to obstructive sleep apnea. Another theory proposed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) absorption impairment due to excessive medication with vitamin A derivatives. Other reports pointed out the importance of obesity, which may cause an impairment of intracranial venous drainage due to elevated right atrial pressure. Patients with medically refractory IIH have traditionally undergone a CSF diversion. Venous outlet impairment on IIH has recently been reported as a causative or contributory cause, and thus focused venoplasty of the stenotic sinus with a stent has emerged as a new treatment strategy. We report the cases of two patients who presented with headache and papilledema with IIH. They successfully underwent stent placement at the stenosis of the transverse sinus and experienced complete resolution of symptoms.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also known as pseudotumor cerebri, is characterized by elevated cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) opening pressure in lumbar puncture [1]. IIH is defined using the following criteria [2]: symptoms of raised intracranial pressure (ICP) (headache, transient visual obscurations, and/or papilledema); no localizing signs, with the exception of abducens nerve palsy; normal computed tomography (CT)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings without evidence of thrombosis; lumbar puncture opening pressure of >25 cmH2O; normal biochemical and cytological composition of the CSF; and no other explanation for the raised intracranial pressure, such as a mass lesion or hydrocephalus.
The pathophysiology of IIH is still unclear [2,3]. Various mechanisms have been proposed, including excess CSF production, impaired CSF reabsorption, and increased cerebral venous pressure [2]. It has been already recognized that patients with IIH frequently have unilateral or bilateral transverse sinus (TS) stenosis [4,5]. Although the question of whether TS stenosis plays a role in the pathophysiology of IIH is a matter of controversy [6-8], a venoplasty of the sinus with stent placement at the stenotic TS with a significant pressure gradient should decrease cerebral venous pressure and reduce intracranial CSF pressure due to the improvement of CSF absorption [6,8-10]. Several studies have been conducted to determine the potential efficacy of such a stent placement treatment. Here we report the cases of two patients with IIH in whom the importance of continuing sinus dilatation with stenting is emphasized.
A 27-year-old Japanese woman (165 cm, 48 kg) presented with progressive headache, vomiting, and diplopia that had begun 2 months earlier. The clinical examination revealed bilateral papilledema and left abducens nerve palsy. The lumbar CSF pressure was 37 cmH2O. We administered an adequate dose of Isosorbide and glycerol as well as analgesic agents for more than 2 months, but any medical treatment brought about no effect. Routine MRI and CT imaging results were normal (Fig. 1A), and an MR venogram showed stenosis of the right TS (Fig. 1B). An angiogram depicted the stenotic TS and occlusion of the left sigmoid sinus (Fig. 1C). The flow from the left TS was found to drain into the vertebral plexus. Intravenous pressure monitoring demonstrated elevated pressure in the superior sagittal sinus (23 mmHg) and a 4 mmHg pressure gradient across the stenosis. We performed a balloon venoplasty of the sinus with a Jackal balloon catheter (6├Ś40 mm; Kaneka Medics, Osaka, Japan) (Fig. 1D, E). Postoperatively the patientŌĆÖs symptoms remarkably improved and the lumbar CSF pressure decreased to 9 cmH2O. On MR venogram taken 1 week after the operation, the patency with small remaining stenosis was confirmed (Fig. 1F), and the patient was discharged without any neurological symptoms.
However, the patient suffered an increased severe headache again the next month. Her lumbar CSF pressure was observed to have risen to 22 cmH2O, and the papilledema was not improved. An MR venogram taken on postoperative day 42 revealed restenosis at the same TS portion (Fig. 1G), and an angiogram also showed the recurrence of stenosis (Fig. 1H). We placed a CarotidWall stent (10├Ś31 mm; Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) (Fig. 1I), and it achieved complete dilatation without the requirements of any boost of balloon dilatation (Fig. 1J). On intravenous pressure monitoring, the 23 mmHg in the superior sagittal sinus with a 6 mmHg pressure gradient across the stenosis improved to 3 mmHg without a pressure gradient after the stenting. The patientŌĆÖs symptoms vanished just after the stenting and had not recurred at the 6-month follow-up. The papilledema was also remarkably improved (Fig. 1K).
The patient was a 17-year-old Japanese girl (163 cm, 54 kg) with severe headache and vomiting that had continued for several months with no history of medication except for anti-pain drugs. Her lumbar CSF pressure was elevated to >50 cmH2O. An MR venogram showed severe stenosis at the right TS and occlusion of the left internal jugular vein (Fig. 2A). An angiogram showed stenosis at the mid-portion of the right TS with an 11-mmHg pressure gradient across the stenosis (Fig. 2B, C). We deployed a Precise Pro RX stent (10├Ś40 mm; Cordis, Fremont, CA, USA), and it achieved complete dilatation without a pressure gradient (Fig. 2D, E). All of the patientŌĆÖs symptoms disappeared just after the operation. Her lumbar CSF pressure dropped to 13 cmH2O on discharge. The papilledema was almost eliminated. A follow-up angiogram taken 1 month later showed no restenosis (Fig. 2F).
The pathophysiology of IIH has been unclear, particularly regarding its etiological dominance in females of reproductive age and its onset triggers. For many years, the pathophysiology of IIH was interpreted as ŌĆ£secondary intracranial hypertension,ŌĆØ [11] and IIH was considered to be caused by brain edema due to obstructive sleep apnea, chronic kidney disease, or connective tissue diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and Beh├¦et disease [12]. Another theory proposed CSF absorption impairment due to excessive medication of vitamin A derivatives, tetracycline antibiotics, and hormonal contraceptives [13]. Other reports [11,14] pointed out the importance of obesity, which may cause an impairment of intracranial venous drainage due to elevated right atrial pressure. According to Kim et al. [15] however, obesity may not be a risk factor for IIH in Asians. Our two young patients were not obese and had no hematological abnormalities (Table 1).
Patients with medically refractory IIH have traditionally undergone a CSF diversion and/or optic nerve sheath fenestration as the first intervention [16,17]. These procedures led to the resolution of visual symptoms in 45% of patients [16] and improvement in 78% of patients [17] The major and minor complication rates were 2.9% and 4.4%, respectively, and the repeated procedure rate was 10.3% [17]. A lumboperitoneal shunt may be the most reasonable and effective way to decrease ICP, but despite the reported high percentage of improvement in visual symptoms, the shunt failure rate after 1 year can be as high as 75% for lumboperitoneal shunts and 50% for ventriculoperitoneal shunts [17]. It has been shown that the lumboperitoneal shunt procedure can carry a 40% complication rate, with recurrence of the initial visual symptoms in up to 33% of patients [18,19].
The impaired venous drainage system due to focal stenosis of a transverse or upper sigmoid sinus has recently become a focus of attention as a possible cause of IIH. It has been recognized that patients with IIH frequently manifest TS stenosis [4,5,9,10]. Most previously reported cases [3,6,20-23]. showed a sinus pressure gradient before and after the stenosis (Table 1). Some reports [3,6] demonstrated the importance of a pressure gradient (>10 mmHg) to decide the indication for sinus stenting. Although our first case might not be an indication for treatment according to such criteria, venoplasty of the sinus dramatically resolved the patientŌĆÖs symptom. We donŌĆÖt know so far why such a subtle imbalance of blood flow and pressure change in the sinus has the possibility to take so strong influence for the symptom. In both our cases, bilateral sinus drainage flow was impaired due to the occlusion or hypoplasty of the left sigmoid sinus as well as the right stenosis of TS. It may be one of the reasons causing such elevation of intracranial pressure. According to the case series in previous papers, the majority of IIH patients showed impairment of the hemilateral sinus, although bilateral stenotic lesions requiring stenting existed in about 8% of patients [6]. However, there were no correlations between the severity and laterality and degree of stenosis.
TS stenosis can be classified into tow types [3,4]: 1) intrinsic discrete stenosis with clearly demarcated intraluminal filling defects secondary to enlarged, partially obstructing intraluminal arachnoid granulations or fibrous septa and 2) long, smooth-tapered narrowing secondary to external compression from swollen brain parenchyma. TS stenosis in IIH patients usually demonstrates the latter pattern, which was also the case in both of our patients. Their TS has a vulnerable wall that is easily collapsed due to intracranial hypertension, as recently proposed based on a mathematic theoretical model [24]. If the TS collapses due to IIH the venous outflow is impaired, which results in further venous hypertension. This situation would cause decreased CSF absorption and causes further increases in intracranial pressure, which then feeds back causing further external compression of the TS and further stenosis [3,25].
Such a vulnerable wall condition was realized in both of our patients. A strong force to expand the sinus with a balloon and stent ŌĆö which is usually needed in the angioplasty of atherosclerotic lesions ŌĆö was not necessary in either patient. Particularly in case 1, the expansion of the sinus after the balloon venoplasty of the sinus seemed to be successful without recoil, but the effect on her symptoms was temporary and the sinus collapsed again within a very short term. This may suggest that the stenosis was not secondarily caused due to the organized granulation tissue or thrombosis, and that the vulnerable wall was easily collapsed again with mechanical external pressure. Although balloon venoplasty alone may yield a temporary effect, it results in early restenosis with symptomatic recurrence like in our first case. We emphasize that continuous dilatation of the sinus with stenting is the ultimate treatment to protect the collapse of the sinus.
Although long-term follow-up of more patients is necessary, it appears that stent placement for a stenotic TS may be a safe and durable treatment to provide symptomatic relief, including the disappearance of headache and restoring vision.
Fig.┬Ā1.
MRI T1 image shows almost normal findings without hydrocephalus of brain swelling (A). MR venogram demonstrates stenosis of the right TS and occlusion of the left sigmoid sinus (B). A right internal cerebral angiogram shows stenosis of the proximal side of the TS (C). After balloon sinusplasty (D), the TS is well dilated (E). An MR venogram taken 1 week later shows the patency of the TS despite remaining mild stenosis (F). The MR venogram taken after the recurrence of symptoms (POD 42) shows restenosis of the TS (G), and a cerebral angiogram showed recurrence of the TS stenosis as well (H). Postoperative angiogram after the deployment of the stent (I) shows the normalized TS (J). The photo of ocular fundus reveals marked improvement of papilledema. Preoperative image (upper) and at the 4-month follow-up (lower) (K). MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TS,
transverse sinus; POD, postoperative day
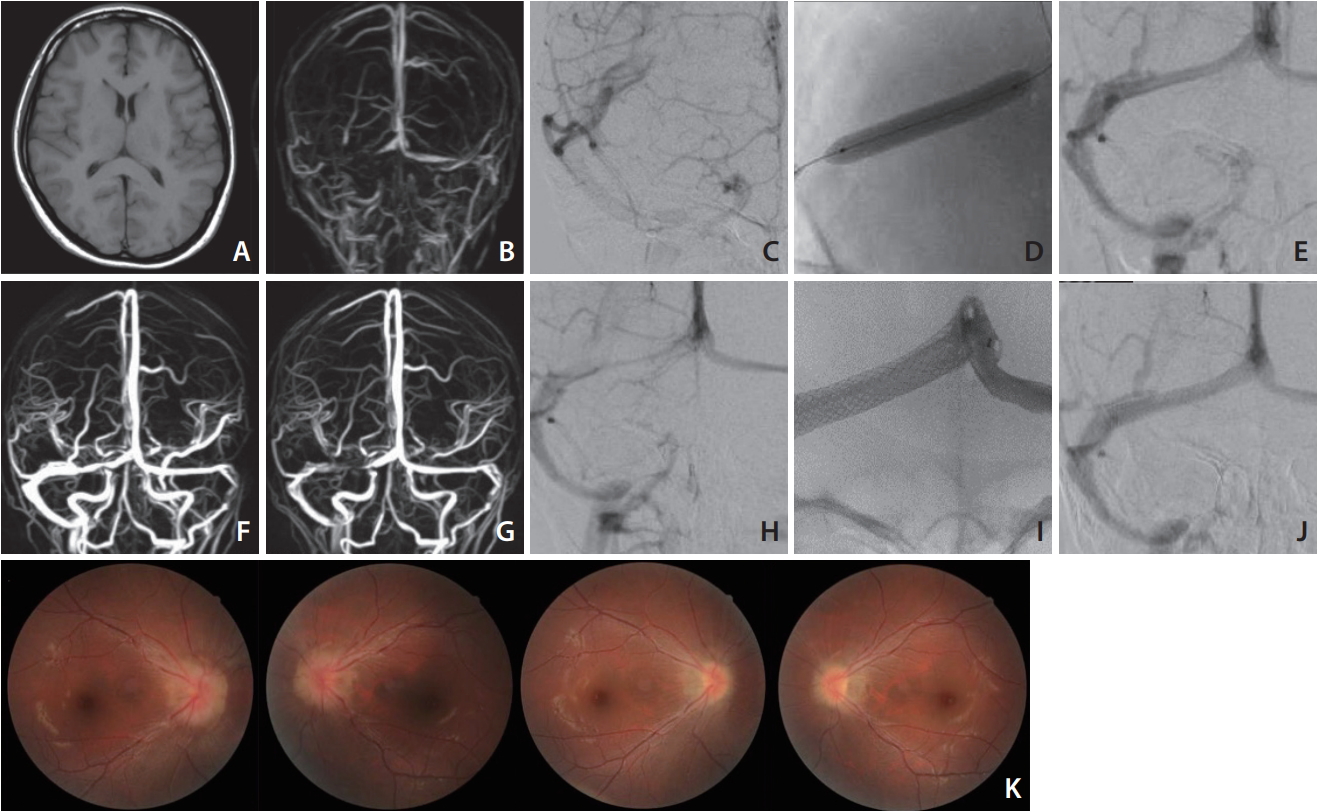
Fig.┬Ā2.
MR venogram shows stenosis of the mid-portion of the right TS and left internal jugular vein (A). Right internal cerebral angiogram demonstrates severe stenosis of the TS (B: antero-posterior [A-P] view, C: lateral view). Angiogram after stenting shows fully dilated TS (D: A-P view, E: lateral view). Follow-up angiogram (lateral view) 1 month later shows no recurrence (F). MR, magnetic resonance; TS, transverse sinus; A-P, antero-posterior.

Table┬Ā1.
Summary of previous reports of venoplasty with a stent for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
| Case | Female | BMI, mean |
Resolved/improved symptoms |
CSF pressure, mean (cmH2O) |
Mean pressure gradient, mean (mmHg) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Headache | Papilledema | Before | After | Before | After | ||||
| Higgins et al. [22](2003) | 12 | 12 | 37 | 7 (58) | 5 (42) | 34 | NR | 19 | 6 |
| Donnet et al. [20] (2008) | 10 | 8 | 27 | 8 (80) | 10 (100) | 40 | 19 | 19 | NR |
| Bussiere et al. [6] (2010) | 10 | 10 | 36 | 10 (100) | 9 (90) | BR | NR | 28 | 11 |
| Ahmed et al. [3] (2011) | 52 | 47 | >30 | 40 (77) | 46 (88) | 33 | 24 | 19 | 1 |
| Fields et al. [21] (2013) | 15 | 15 | 39 | 10 (67) | 15 (100) | NR | NR | 24 | 4 |
| Kumpe et al. [19] (2012) | 18 | 12 | 32 | 10 (56) | 16 (89) | 40 | NR | 21 | 3 |
| Radvany et al. [23] (2013) | 12 | 11 | 33 | 7 (58) | 11 (92) | 40 | NR | 12 | 1 |
| Our case 1 (2018) | 1 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 37 | 9 | 23 | 19 | |
| Our case 2 (2018) | 1 | 20 | 1 | 1 | >50 | 13 | 22 | 11 | |
References
1. Puffer RC, Mustafa W, Lanzino G. Venous sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension; a review of the literature. J Neurointervent Surg 2013;5:483-486.

2. Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 2002;59:1492-1495.


3. Ahmed RM, Wilkinson M, Parker GD, Thurtell MJ, Macdonald J, McCluskey PJ, et al. Transverse sinus stenting for idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a review of 52 patients and of model predictions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:1408-1414.



4. Farb RI, Vanek I, Scott JN, Mikulis DJ, Willinsky RA, Tomlinson G, et al. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: the prevalence and morphology of sinovenous stenosis. Neurology 2003;60:1418-1424.


5. Higgins JN, Gillard JH, Owler BK, Harkness K, Pickard JD. MR venography in idiopathic intracranial hypertension: unappreciated and misunderstood. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004;75:621-625.



6. Bussi├©re M, Falero R, Nicolle D, Proulx A, Patel V, Pelz D. Unilateral transverse sinus stenting of patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2010;31:645-650.



7. King JO, Mitchell PJ, Thomson KR, Tress BM. Manometry combined with cervical puncture in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology 2002;58:26-30.


8. Rohr A, D├Črner L, Stingele R, Buhl R, Alfke K, Jansen O. Reversibility of venous sinus obstruction in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2007;28:656-659.


9. Higgins JN, Owler BK, Cousins C, Pickard JD. Venous sinus stenting for refractory benign intracranial hypertension. Lancet 2002;359:228-230.


10. Rajpal S, Niemann DB, Turk AS. Transverse venous sinus stent placement as treatment for benign intracranial hypertension in a young male: case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg 2005;102(3 suppl):342-346.

11. Binder DK, Horton JC, Lawton MT, McDermott MW. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurosurgery 2004;54:538-551 ; discussion 551-552


12. Acheson JF. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and visual function. Br Med Bull 2006;79-80 233-240.

13. Warner JE, Larson AJ, Bhosale P, Digre KB, Henley C, Alder SC, et al. Retinol-binding protein and retinol analysis in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with and without idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neuroophthalmol 2007;27:258-262.


14. Karahalios DG, Rekate HL, Khayata MH, Apostolides PJ. Elevated intracranial venous pressure as a universal mechanism in pseudotumor cerebri of varying etiologies. Neurology 1996;46:198-202.


15. Kim TW, Choung HK, Khwarg SI, Hwang JM, Yang HJ. Obesity may not be a risk factor for idiopathic intracranial hypertension in Asians. Eur J Neurol 2008;15:876-879.


16. Banta JT, Farris BK. Pseudotumor cerebri and optic nerve sheath decompression. Ophthalmology 2000;107:1907-1912.


17. Satti SE, Leishangthem L, Chaudry MI. Meta-analysis of CSF diversion procedures and dural venous sinus stenting in the setting of medically refractory idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015;36:1899-1904.



18. McGirt MJ, Woodworth G, Thomas G, Miller N, Williams M, Rigamonti D. Cerebrospinal fluid shunt placement for pseudotumor cerebri-associated intractable headache: predictors of treatment response and an analysis of long-term outcomes. J Neurosurg 2004;101:627-632.


19. Kumpe DA, Bennett JL, Seinfeld J, Pelak VS, Chawla A, Tierney M. Dural sinus stent placement for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurosurg 2012;116:538-548.


20. Donnet A, Metellus P, Levrier O, Mekkaoui C, Fuentes S, Dufour H, et al. Endovascular treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: clinical and radiologic outcome of 10 consecutive patients. Neurology 2008;70:641-647.


21. Fields JD, Javedani PP, Falardeau J, Nesbit GM, Dogan A, Helseth EK, et al. Dural venous sinus angioplasty and stenting for the treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. J Neurointerv Surg 2013;5:62-68.


22. Higgins JN, Cousins C, Owler BK, Sarkies N, Pickard JD. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension: 12 cases treated by venous sinus stenting. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2003;74:1662-1666.



23. Radvany MG, Solomon D, Nijjar S, Subramanian PS, Miller NR, Rigamonti D, et al. Visual and neurological outcomes following endovascular stenting for pseudotumor cerebri associated with transverse sinus stenosis. J Neuroophthalmol 2013;33:117-122.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 13 Crossref
- 9,153 View
- 240 Download
- Related articles in NI
-
Endovascular Treatment of Symptomatic Basilar Artery Stenosis2023 November;18(3)
Endovascular Treatment for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Nationwide Survey in Korea2020 March;15(1)
Endovascular Treatment of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Report.2009 February;4(1)