 |
 |
- Search
| Neurointervention > Volume 18(2); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Among the various perspectives on cerebrovascular diseases, hemodynamic analysisŌĆöwhich has recently garnered interestŌĆöis of great help in understanding cerebrovascular diseases. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis has been the primary hemodynamic analysis method, and studies on cerebral aneurysms have been actively conducted. However, owing to the intrinsic limitations of the analysis method, the role of wall shear stress (WSS), the most representative parameter, remains controversial. High WSS affects the formation of cerebral aneurysms; however, no consensus has been reached on the role of WSS in the growth and rupture of cerebral aneurysms. Therefore, this review aimed to briefly introduce the up-to-date results and limitations made through CFD analysis and to inform the need for a new hemodynamic analysis method.
Because the rupture of a cerebral aneurysm has severe consequences, there is a strong tendency to treat it before rupture. However, the diagnosis of unruptured cerebral aneurysms has increased with the development of diagnostic modalities, prompting the question of whether all unruptured cerebral aneurysms should be treated. As the adverse effects of treatment cannot be disregarded, it is important to select unruptured cerebral aneurysms that require treatment on a reasonable basis.
Therefore, selecting and treating unruptured cerebral aneurysms at a high risk of rupture is critical. Several studies have been conducted to predict the risk of cerebral aneurysm rupture from various perspectives. Morphological, pathophysiological, and clinical factors have been suggested as the basis for judgment; however, explanations in the field of hemodynamics have only recently been of focus [1-12]. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the most commonly used method in hemodynamic studies.
With the advent of CFD analysis in clinical practice, hemodynamic studies of cerebral aneurysms have become active. CFD analysis is widely used in mechanical engineering; however, because the shape of the cerebral aneurysms was precisely implemented with digital subtraction angiography (DSA), it can be introduced in the hemodynamic field of cerebral aneurysms.
The fundamental principle of CFD analysis involves discretizing a fluid domain into control volumes and solving the governing equations that describe fluid motion. These governing equations encompass the continuity equation and the Navier-Stokes equation, which are derived from the conservation laws of mass and momentum. The continuity equation and the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation are expressed as follows:
Continuity equation: Ōłé Žü Ōłé t + Ō¢Į ┬Ę Žü ╬Į ŌåÆ = S m
Incompressible Navier-Stokes equation: Žü D ╬Į ŌåÆ D t = ŌłÆ Ō¢Į P + ╬╝ Ō¢Į 2 ╬Į ŌåÆ + Žü g ŌåÆ
where ╬Į ŌåÆ g ŌåÆ
CFD analysis proves to be an invaluable tool for quantitatively assessing blood flow within cerebral arteries and aneurysms. The velocity obtained through CFD analysis can be utilized in diverse applications pertaining to cerebral aneurysms. Fig. 2 demonstrates an example of velocity evaluation in the circle of Willis and a cerebral aneurysm.
Several assumptions were premised for the CFD analysis introduced for the hemodynamics of the intracranial vessels. Blood flow was assumed to be Newtonian for the convenience of simulation in the CFD analysis. In addition, the blood vessel was assumed to be a rigid wall in the CFD analysis. Therefore, the effects of the wall thickness and material properties of the blood vessels on the formation, growth, and rupture of cerebral aneurysms were excluded, and only the effect of blood flow was considered. However, since a cerebral aneurysm is a morphological change in blood vessels, it cannot be assumed that blood vessels do not change.
In addition to these intrinsic limitations of CFD analysis, it is not patient-specific. To analyze natural phenomena, the material properties of the target must be identified. However, the material properties of blood vessels used in previous studies were not patient-specific and were obtained from a cohort of healthy patients. Each patient had different material properties and vessel thicknesses. Furthermore, the velocity, viscosity, and blood pressure corresponding to the boundary conditions for the CFD analysis had different values for each patient. To date, studies have assumed that the boundary conditions are uniformly the same value for each study.
CFD analysis is based on several assumptions, which can be an intrinsic limitation of this analysis method. Nevertheless, CFD analysis is the underlying method for hemodynamic analysis, and we need to study the most important parameters in the CFD analysis of cerebral aneurysms.
WSS is among the most important hemodynamic parameters in CFD analysis and is a frictional force from the blood flow tangential to the arterial lumen. The relative difference in velocity between two parallel objects creates shear stress [13]. In the normal range (1.5ŌĆō2.5 Pa) of WSS, endothelial function is regulated [14]. However, if the WSS is outside the normal range, histological changes related to the aneurysm may occur. Although WSS is conventionally associated with the natural history (formation, growth, and rupture) of cerebral aneurysms, the effect of the WSS on each natural history remains controversial.
Several studies utilizing animal models have identified a high WSS as an important parameter in aneurysm formation [15-21]. In addition, Can and Du [22] reported a strong positive correlation between elevated WSS and the location of aneurysm formation in their systematic review and meta-analysis. The authors included 19 studies that investigated WSS using CFD for geometrical models of intracranial aneurysms and found that high WSS was associated with formation and low WSS was associated with rupture of intracranial aneurysms [22].
Unlike the consensus that aneurysm formation occurs in regions with high WSS, the exact role of WSS in the growth and rupture of intracranial aneurysms is controversial. It is unclear whether a high or low WSS plays a principal role in growth and rupture. There are ŌĆ£highŌĆØ and ŌĆ£lowŌĆØ WSS theories, both of which explain why the hemodynamic environment within the aneurysm interacts with the cellular elements of the aneurysm wall, resulting in further weakening. However, the differences revolve around the mechanisms that cause the weakening of the weakening [21].
According to the high WSS theory, high WSS causes endothelial injury and initiates processes of wall remodeling and degeneration [13]. Castro et al. [23] investigated anterior communicating artery aneurysms and suggested that aneurysms with a high WSS were more likely to rupture than those with a low WSS. Cebral et al. [24] reported that a high WSS is related to aneurysmal rupture. Hassan et al. [25] suggested that aneurysms rupture because blood flow impingement on the aneurysmal wall produced a high WSS.
In contrast, the low WSS theory suggests that stagnation of blood within the aneurysm leads to red blood cell aggregation and build-up of platelets and leukocytes [21]. These changes cause intimal damage and inflammatory cell infiltration of the vessel wall, leading to wall degeneration and reduced ability to withstand physiological hemodynamic forces [21]. Several studies have found that aneurysm growth and rupture are more likely to occur in regions with abnormally low WSS [2,21,26,27].
To unify the controversial results of previous studies on WSS, Meng et al. [28] published a review article. They indicated that the leading controversial reports on WSS depended on differences in the natural history of each analyzed aneurysm [28]. They hypothesized that the mural cell-mediated pathway associated with high WSS may be responsible for the growth and rupture of small or secondary bleb aneurysm phenotypes, whereas the inflammation-mediated pathway associated with low WSS may be responsible for the growth and rupture of large atherosclerotic and thrombotic cerebral aneurysm phenotypes [28]. Furthermore, although the exact mechanism involved is unknown, Cebral et al. [29] recently supported the idea that different hemodynamic conditions are associated with different aneurysm phenotypes.
However, some researchers have reported no significant difference in the WSS values between stable and unstable aneurysms. In their investigation of 178 patients with 198 unruptured cerebral aneurysms, Ramachandran et al. [30] found that low WSS did not statistically discriminate between stable and unstable aneurysms. Based on their study of 33 unruptured aneurysms, Sforza et al. [31] suggested that concentrated inflow streams blown into complex intrasaccular flow patternsŌĆöcausing nonuniform WSS distributionsŌĆömay represent the characteristics of a hemodynamic environment that predisposes the aneurysm to grow.
As mentioned previously, high WSS experienced during aneurysm formation may lead to a low WSS as the geometry of the aneurysm changes [28]. It is unknown whether this inconsistency is a result of intrinsic study limitations or inherent complexity and heterogeneity of the biological mechanisms involved in aneurysm evolution [32,33]. Meng et al. [28] explained that both high and low WSS can independently lead to intracranial aneurysm growth and rupture, albeit through different biological mechanisms. However, despite the explanation, it is not yet possible to predict the state in which a high WSS will cause growth or rupture, and that in which a low WSS will cause growth and rupture. Clinicians must predict where growth or rupture will occur in the same patient, either in the high- or low-WSS region.
If the intrinsic limitations of CFD analysis lead to inconsistencies and controversial results, it may be helpful to apply other analytical methods.
There are several hemodynamic parameters in CFD analysis. Previous hemodynamic studies define several hemodynamic parameters associated with natural history of cerebral aneurysms. Among the various hemodynamic parameters, oscillatory shear index (OSI) and WSS gradient (WSSG) have demonstrated their role in aneurysm rupture risk analysis.
OSI is a dimensionless parameter that indicates how the direction of WSS changes at a specific location during a cardiac cycle.
Previous studies reported that a higher OSI was observed in ruptured than in unruptured aneurysms, or high OSI corresponded to the rupture point [27]. They suggested that low WSS and high OSI predict rupture risk of cerebral aneurysms [27, 28].
WSSG is defined as the spatial derivative of WSS along the direction of flow. It can be thought of as the change in WSS along the length of the vessel [14]. Accelerating flow creates a positive WSSG, while decelerating flow creates a negative WSSG. Meng et al. [28] explained that the formation of cerebral aneurysms occurs in regions exposed to high WSS with a positive WSSG in the mural cell-mediated pathway theory.
As shown in the defintions presented above, both OSI and WSSG are secondary parameters derived from the concept of WSS. Cho et al. [2] defined a novel parameter, the so-called combined hemodynamic parameter, associated with aneurysmal rupture. Similarly, it was derived from the perception of WSS.
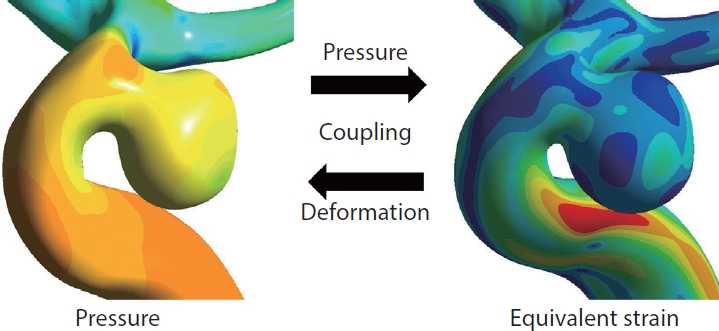
A cerebral aneurysm is a structural change that occurs when the shape of blood vessels changes due to the influence of blood flow. However, because CFD analysis assumes rigid blood vessel walls, the effects of the blood vessels are ignored. In contrast, fluid-structure interaction (FSI) analysis assumes that the blood vessel is not rigid but deformable; therefore, the effects of the wall thickness and mechanical properties of the aneurysms can be evaluated in a more realistic manner. In FSI analysis, using the pressure induced by the blood flow calculated from CFD analysis, the deformation of a cerebral artery can be evaluated by calculating the strain (Fig. 3). Strain represents how much a cerebral artery is stretched. Higher strain indicates that the blood vessel is more severely stretched. FSI analysis involves complex computational techniques, and the results depend on the thickness or elastic modulus of the vessel, which is difficult to obtain using common diagnostic imaging devices [34]. Nevertheless, several hemodynamic studies have used FSI analysis [35-37].
Cho et al. [35] suggested in FSI analysis that strain was more effective than WSS in predicting the rupture risk of cerebral aneurysms. In addition, unlike WSS, which shows inconsistency as it pregresses from formation to growth and rupture, high strain continues to be involved in the natural history of cerebral aneurysms. Kim et al. [36] reported that strain has an important role in the formation of cerebral aneurysms.
Despite overcoming several intrinsic limitations of CFD analysis, FSI analysis still has some limitations. The material properties and wall thickness of the cerebral artery are greatly influenced by the deformation of the cerebral artery. However, because material properties and wall thicknesses vary from person to person, it is difficult to determine the material properties and wall thicknesses of individuals. Although there have been efforts to study the material properties and wall thickness of the cerebral artery, there is still a need for further research in this area.
Both CFD and FSI analyses use computational simulations, and 3D angiography should be used as the source data. Therefore, the quality of source data is very important. 3D rotational angiography (3DRA) from DSA provides the highest resolution (approximately 0.2ŌĆō0.3 mm) but is difficult to perform repeatedly as an invasive modality [38]. Modern multidetector computed tomographic angiography (CTA) provides resolutions of approximately 0.4ŌĆō0.5 mm, but has a critical disadvantage involving artifacts from nearby bone [38]. Time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) offers a poorer resolution of approximately 0.6ŌĆō0.8 mm and has artifacts due to slowly recirculating flows that may be present in some aneurysms [38].
In a recent study comparing 3DRA and CTA, Lauric et al. [39] reported significant differences in low WSS between the 2 modalities. In addition, unlike CTA and MRA, 3DRA is performed by injecting contrast agents directly into the arteries, which may affect their tortuosity.
These can be sources of variability among modalities, which can affect the results of hemodynamic analysis. Therefore, research on the differences in the results of hemodynamic studies according to differences in modalities needs to be conducted carefully.
The main limitation of hemodynamic analysis, which is being studied worldwide, is that standardized research methodologies have not been established. Standardized methodologies have not been presented at all stages, such as segmentation, meshing, and solvers, which are the basic stages of hemodynamic analysis or the selection of image modalities used as source data. In addition, the conditions necessary for analysis, such as the thickness and material properties of blood vessels, and inlet conditions are not yet strictly patient-specific. A consensus on these limitations must be attained through discussions with researchers worldwide.
Notes
Fund
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2021R1F1A1049435).
Fig.┬Ā1.
General process of computed fluid dynamics (CFD). Following the reconstruction of the 3-dimensional (3D) model of a cerebral artery, meshing and boundary condition applications are performed. Hemodynamic parameters are then computed.

Fig.┬Ā2.
Examples of computed fluid dynamics (CFD) results. Velocity evaluation in a circle of Willis (A) and a cerebral aneurysm (B). The velocity obtained through CFD analysis is color-coded and used for calculating hemodynamic parameters.

Fig.┬Ā3.
Explanation of fluid-structure interaction (FSI) process. In FSI analysis, the strain used to evaluate the deformation of the cerebral artery is calculated using the pressure on the blood vessels induced by blood flow. The values of pressure in computed fluid dynamics analysis and equivalent strain in FSI analysis are color-coded.
REFERENCES
1. Cebral J, Ollikainen E, Chung BJ, Mut F, Sippola V, Jahromi BR, et al. Flow conditions in the intracranial aneurysm lumen are associated with inflammation and degenerative changes of the aneurysm wall. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2017;38:119-126.



2. Cho KC, Choi JH, Oh JH, Kim YB. Prediction of thin-walled areas of unruptured cerebral aneurysms through comparison of normalized hemodynamic parameters and intraoperative images. Biomed Res Int 2018;2018:3047181



3. Dhar S, Tremmel M, Mocco J, Kim M, Yamamoto J, Siddiqui AH, et al. Morphology parameters for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Neurosurgery 2008;63:185-196 discussion 196-197



4. Feigin VL, Rinkel GJ, Lawes CM, Algra A, Bennett DA, van Gijn J, et al. Risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage: an updated systematic review of epidemiological studies. Stroke 2005;36:2773-2780.


5. Fr├Čsen J, Piippo A, Paetau A, Kangasniemi M, Niemel├ż M, Hernesniemi J, et al. Remodeling of saccular cerebral artery aneurysm wall is associated with rupture: histological analysis of 24 unruptured and 42 ruptured cases. Stroke 2004;35:2287-2293.


6. Huang ZQ, Meng ZH, Hou ZJ, Huang SQ, Chen JN, Yu H, et al. Geometric parameter analysis of ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in patients with symmetric bilateral intracranial aneurysms: a multicenter CT angiography study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2016;37:1413-1417.



7. Kleinloog R, de Mul N, Verweij BH, Post JA, Rinkel GJE, Ruigrok YM. Risk factors for intracranial aneurysm rupture: a systematic review. Neurosurgery 2018;82:431-440.


8. Raghavan ML, Ma B, Harbaugh RE. Quantified aneurysm shape and rupture risk. J Neurosurg 2005;102:355-362.


9. Rahman M, Smietana J, Hauck E, Hoh B, Hopkins N, Siddiqui A, et al. Size ratio correlates with intracranial aneurysm rupture status: a prospective study. Stroke 2010;41:916-920.


10. Ujiie H, Tachibana H, Hiramatsu O, Hazel AL, Matsumoto T, Ogasawara Y, et al. Effects of size and shape (aspect ratio) on the hemodynamics of saccular aneurysms: a possible index for surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 1999;45:119-129 discussion 129-130


11. Yasuda R, Strother CM, Taki W, Shinki K, Royalty K, Pulfer K, et al. Aneurysm volume-to-ostium area ratio: a parameter useful for discriminating the rupture status of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2011;68:310-317 discussion 317-318

12. Zheng Y, Xu F, Ren J, Xu Q, Liu Y, Tian Y, et al. Assessment of intracranial aneurysm rupture based on morphology parameters and anatomical locations. J Neurointerv Surg 2016;8:1240-1246.


13. Soldozy S, Norat P, Elsarrag M, Chatrath A, Costello JS, Sokolowski JD, et al. The biophysical role of hemodynamics in the pathogenesis of cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Neurosurg Focus 2019;47:E11

14. Dolan JM, Kolega J, Meng H. High wall shear stress and spatial gradients in vascular pathology: a review. Ann Biomed Eng 2013;41:1411-1427.



15. Alfano JM, Kolega J, Natarajan SK, Xiang J, Paluch RA, Levy EI, et al. Intracranial aneurysms occur more frequently at bifurcation sites that typically experience higher hemodynamic stresses. Neurosurgery 2013;73:497-505.


16. Chen H, Selimovic A, Thompson H, Chiarini A, Penrose J, Ventikos Y, et al. Investigating the influence of haemodynamic stimuli on intracranial aneurysm inception. Ann Biomed Eng 2013;41:1492-1504.


17. Gao L, Hoi Y, Swartz DD, Kolega J, Siddiqui A, Meng H. Nascent aneurysm formation at the basilar terminus induced by hemodynamics. Stroke 2008;39:2085-2090.



18. Geers AJ, Morales HG, Larrabide I, Butakoff C, Bijlenga P, Frangi AF. Wall shear stress at the initiation site of cerebral aneurysms. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2017;16:97-115.


19. Meng H, Swartz DD, Wang Z, Hoi Y, Kolega J, Metaxa EM, et al. A model system for mapping vascular responses to complex hemodynamics at arterial bifurcations in vivo. Neurosurgery 2006;59:1094-1100 discussion 1100-1101



20. Meng H, Wang Z, Hoi Y, Gao L, Metaxa E, Swartz DD, et al. Complex hemodynamics at the apex of an arterial bifurcation induces vascular remodeling resembling cerebral aneurysm initiation. Stroke 2007;38:1924-1931.



21. Sforza DM, Putman CM, Cebral JR. Hemodynamics of cerebral aneurysms. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 2009;41:91-107.



22. Can A, Du R. Association of hemodynamic factors with intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture: systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 2016;78:510-520.

23. Castro MA, Putman CM, Sheridan MJ, Cebral JR. Hemodynamic patterns of anterior communicating artery aneurysms: a possible association with rupture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009;30:297-302.



24. Cebral JR, Mut F, Weir J, Putman C. Quantitative characterization of the hemodynamic environment in ruptured and unruptured brain aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32:145-151.



25. Hassan T, Timofeev EV, Saito T, Shimizu H, Ezura M, Matsumoto Y, et al. A proposed parent vessel geometry-based categorization of saccular intracranial aneurysms: computational flow dynamics analysis of the risk factors for lesion rupture. J Neurosurg 2005;103:662-680.


26. Nixon AM, Gunel M, Sumpio BE. The critical role of hemodynamics in the development of cerebral vascular disease. J Neurosurg 2010;112:1240-1253.


27. Xiang J, Natarajan SK, Tremmel M, Ma D, Mocco J, Hopkins LN, et al. Hemodynamic-morphologic discriminants for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 2011;42:144-152.



28. Meng H, Tutino VM, Xiang J, Siddiqui A. High WSS or low WSS? Complex interactions of hemodynamics with intracranial aneurysm initiation, growth, and rupture: toward a unifying hypothesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2014;35:1254-1262.



29. Cebral JR, Detmer F, Chung BJ, Choque-Velasquez J, Rezai B, Lehto H, et al. Local hemodynamic conditions associated with focal changes in the intracranial aneurysm wall. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2019;40:510-516.


30. Ramachandran M, Retarekar R, Raghavan ML, Berkowitz B, Dickerhoff B, Correa T, et al. Assessment of image-derived risk factors for natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg 2016;124:288-295.


31. Sforza DM, Kono K, Tateshima S, Vi├▒uela F, Putman C, Cebral JR. Hemodynamics in growing and stable cerebral aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg 2016;8:407-412.


32. Cebral JR, Meng H. Counterpoint: realizing the clinical utility of computational fluid dynamics--closing the gap. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33:396-398.



33. Robertson AM, Watton PN. Computational fluid dynamics in aneurysm research: critical reflections, future directions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33:992-995.



34. Murayama Y, Fujimura S, Suzuki T, Takao H. Computational fluid dynamics as a risk assessment tool for aneurysm rupture. Neurosurg Focus 2019;47:E12

35. Cho KC, Yang H, Kim JJ, Oh JH, Kim YB. Prediction of rupture risk in cerebral aneurysms by comparing clinical cases with fluid-structure interaction analyses. Sci Rep 2020;10:18237



36. Kim JJ, Yang H, Kim YB, Oh JH, Cho KC. The quantitative comparison between high wall shear stress and high strain in the formation of paraclinoid aneurysms. Sci Rep 2021;11:7947



37. Yang H, Cho KC, Kim JJ, Kim JH, Kim YB, Oh JH. Rupture risk prediction of cerebral aneurysms using a novel convolutional neural network-based deep learning model. J Neurointerv Surg 2023;15:200-204.