 |
 |
- Search
| Neurointervention > Volume 13(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Neurointerventional radiology procedures often require a long time to perform. Patient radiation dose is an important issue due to the hazards of ionizing radiation. The objective of this study was to measure the peak skin dose (PSD) and effective dose to estimate the deterministic and stochastic effects of a therapeutic interventional neuroradiologic procedure.
Materials and Methods
The cumulative dose (CD) and dose area product (DAP) were automatically recorded by a fluoroscopic machine and collected prospectively between April and November 2015. The study included 54 patients who underwent therapeutic neurointerventional radiology procedures. The CD of each patient was used to estimate the peak skin dose and the DAP was also calculated to estimate the effective dose.
Results
The average estimated peak skin dose was 1,009.68 mGy. Two patients received radiation doses of more than 2 Gy, which is the threshold that may cause skin complications and radiation-induced cataract. The average effective dose was 35.32 mSv. The majority of patients in this study (85.2%) who underwent therapeutic neurointerventional radiologic procedures received effective doses greater than 20 mSv.
Conclusion
Not all therapeutic neurointerventional radiology procedures are safe from deterministic complications. A small number of patients received doses above the threshold for skin complications and radiation induced cataract. In terms of stochastic complications, most neurointerventional radiology procedures in this study were quite safe in terms of radiation-induced cancer.
Neurointerventional radiology procedures are increasingly used. Because of the complexity in the anatomy and procedures, neurointerventional radiology procedures often require a long time to perform. Patient radiation dose is an important issue due to the hazards of ionizing radiation. The two types of radiation effects that are a hazard to the patient are the deterministic and stochastic effects [1]. The deterministic effect is defined as the effect related to the radiation dose causing localized injury to the tissue when the radiation dose reaches the dose threshold [2,3]. A greater radiation dose will cause more injury in the deterministic effect. Conversely, the stochastic effect is defined as the effect without reaching the dose threshold, but the effect may occur over time. There is no threshold for the stochastic effect, but increased radiation causes a greater risk for this effect to occur. The risk for cancer-associated radiation is an example of the stochastic effect [4].
Based on the background knowledge of the radiation effect, many retrospective and prospective studies found some patients who underwent neurointerventional radiology procedures may have received a very high radiation dose [5-7] that caused a permanent skin complication or radiation-induced cataract [3]. Moreover, in terms of the stochastic radiation effect the radiation dose from the procedure will increase the risk for cancer as well [8-10]. Knowing the radiation dose and the effects that may occur from neurointerventional radiology procedures can raise the concern of the physician and the interventionist to be aware of the complications of ionizing radiation and provide better care of the patients in daily clinical practice. There are many measurements related to the radiological dose. The absorbed dose is measured in Gray (Gy) units. Fluoroscopic time describes the number of images obtained in each procedure. This parameter provides a poor estimation of skin dose because it does not depend on X-ray field size, position, or patient size [11]. Dose area product (DAP) describes the total dose of X-ray flux in the beam [12]. The DAP does not correlate well with the skin dose because there is no effect of the distance in this parameter. However, this parameter correlates well with the stochastic effect [13-16]. The effective dose [17,18] reflects the sum of the dose equivalents (Sv) for each organ in the body, weighted by a factor to reflect radio-sensitivity. The effective dose estimates the whole-body dose required to produce the same stochastic risk as the partial-body dose that is actually delivered by a radiological examination or procedure.
The purpose of our study was to quantify the estimated peak skin dose (PSD) to estimate the deterministic effect and effective dose to estimate the stochastic effect. A previous study showed a good correlation in estimating the PSD using the cumulative dose (CD) and the effective dose using the DAP [19]. Therefore, the main factor in our study is to determine these two parameters to calculate the estimated PSD and effective dose.
This study used prospectively collected data from all patients older than 15 years who underwent a therapeutic neurointerventional radiology procedure at Songklanagarind Hospital from April to November 2015. Written informed consent detailing the procedure was obtained from all patients before intervention. The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University (IRB No. 58-165-07-4).
PSD describes the maximal radiation dose at any point of the patientŌĆÖs skin which is the best predictor to evaluate a local complication from the deterministic effect. However, measuring this parameter is difficult and not practical in daily clinical practice [19,20]. CD is the air kerma value at a specific point [21]. CD does not include the tissue backscatter. The center may not present the actual area of the patientŌĆÖs skin causing inaccuracy in the measurement of the skin dose. CD is usually greater than the actual PSD. However, CD does correlate well with the actual skin dose [19], which is measured in Gy units. By knowing the CD and dose index we can calculate the estimated skin dose [19]. Dose index is a ratio between the CD at an interventional reference point (IRP) and the real PSD. This parameter is specific for each procedure and operator [22,23]. Due to the difficulty of quantifying the PSD, we can use the dose index to calculate the PSD. If we know the dose index and CD at the IRP, we can calculate the estimated PSD. From a prior study, the dose index for a body interventional procedure is about 0.49ŌĆō1.0 which is a very wide range. Fortunately, a more precise dose index in neurointerventional radiology procedures is about 0.51ŌĆō0.56 [19]. In our study we used 0.56 to calculate the estimated PSD.
One fluoroscopic machine (biplanes digital subtraction angiography, Allura FD20; Philips, Best, The Netherlands) was used for the neurointerventional radiology procedure. At the end of the procedure, the cumulative dose, dose area product, fluoroscopic time, diagnosis, and the procedure time were collected instantly and automatically by the computer system. The effective dose was calculated for each patient by multiplication of DAP using a conversion coefficient of 0.087 [24]. The PSD was estimated by calculation of the CD multiplied by the dose index of 0.56.
Data were compiled into a spreadsheet (Microsoft Office Excel 2010; Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA), and a descriptive analysis was performed using statistical software (R version 3.1.2 for windows; Free Software Foundation, Inc., Boston, MA, USA). The correlation was calculated using the statistical software.
Fifty-four patients were enrolled in this study. Twenty-eight patients (51.9%) were female. The mean age of the patients was 48 years (range, 15 to 82 years). The majority of diagnoses were aneurysm (42.6%) and arteriovenous malformation (42.6%). The other diagnoses included dural carotid cavernous fistula, dural arteriovenous fistula, and juvenile angiofibroma in 9.3, 3.7, and 1.9%, respectively. Almost half of the procedures (46.3%) were glue embolization. Other procedures included aneurysmal coiling, stent assisted coiling, balloon embolization, coil embolization, and polyvinyl alcohol embolization in 35.2, 7.4, 5.6, 3.7, and 1.9%, respectively. A summary of the diagnoses and procedures are in Table 1.
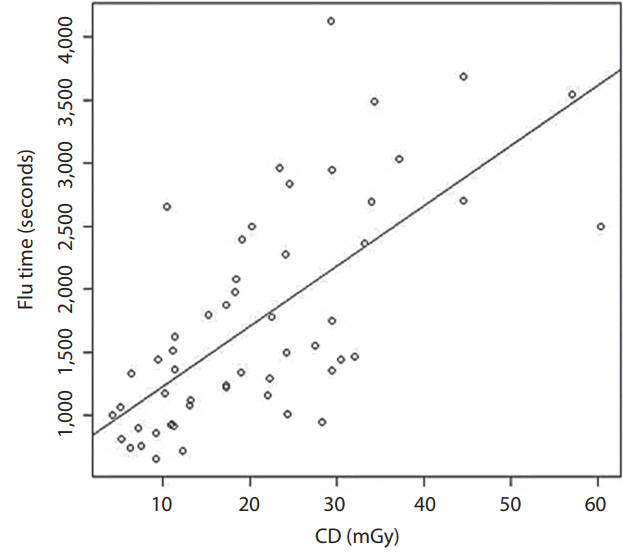
Our CD was the summation of the frontal and lateral fluoroscopy. The mean CD was 1,803. By using the dose index of 0.56, the estimated mean skin dose was 1,009.68 mGy. The mean DAP was 406.19 Gy┬Ęcm2. The mean effective dose was 35.32 mSv when we used the coefficient of 0.087 mSv/mGy┬Ęcm2. The mean fluoroscopic time was 20.9 minutes. The conclusions of the CD, DAP, estimated PSD, effective dose, and fluoroscopic time are shown in Table 2. The correlation between fluoroscopic time and CD at the IRP is also presented in Fig. 1.
When using the subgroup analysis depending on the procedure, the procedure that had the highest radiation dose was presumably the stent-assisted coiling showing a mean CD of 2,222.5. However, the maximum radiation dose was found in coiling that showed a maximal CD of 4,130.7. The subgroup analysis conclusion is described in Table 3. In terms of dosimetry, the parameter that indicates the deterministic effect is the PSD, and the stochastic effect is the effective dose. By using a dose index of 0.56 and a conversion coefficient of 0.087, the estimated PSDs and effective doses are shown in Table 4.
Concerning the deterministic effect outcome, two patients (3.7%) received the estimated PSD that exceeded the threshold of 2 Gy. One patient had stent-assisted coiling performed, and the other had a coiling procedure. Twenty patients (37%) had doses higher than 1 Gy. For the stochastic effect outcome, 14.8% received an effective dose not greater than 20 mSv, and 85.2% received an effective dose greater than 20 mSv (Table 5).
Unlike a CT scan or plain radiograph, fluoroscopic procedures are more prone to cause localized effects due to the ionizing radiation which is a deterministic effect. A single dose that exceeds 2 Gy may cause skin epilation or cataract. Permanent epilation and skin necrosis may appear if acute radiation doses are higher than 7 and 12 Gy, respectively. Protracted exposure to the eye may cause cataract if the dose exceeds 4 Gy within 3 months or 5.5 Gy over a period of time longer than 3 months [3]. A few previous studies showed that higher values of the dose threshold caused cataract or even permanent skin injury [6,7,19].
A previous study in Thailand by Sangkrut et al. [25] studied radiation dose in interventional procedures. However, they did not include PSD, which is a more accurate predictor of the deterministic effect. This study is the first to collect the radiation dose in therapeutic neurointerventional radiology procedures and focus on PSD in Thailand. Although we could not determine the real skin dose due to a lack of instruments for measurement, we used the dose index calculated from a previous study [19] to estimate the PSD, which is likely to be more accurate than the previous study in Thailand [25].
Our results demonstrated that two patients received a PSD higher than 2 Gy, which is the threshold that may cause skin epilation and a single dose for radiation-induced cataract [3]. The procedures that involved high radiation doses were stent assisted coiling and coiling. The explanations for the high doses in these two procedures might be the complexity of the techniques. Fig. 1 shows a scatter plot of the correlation between fluoroscopic time and CD at the reference point by implying that more fluoroscopic time was related to the complexity of the procedure. A good correlation between the CD and fluoroscopic time indicates that the complexity of the procedure may be more prone to exceed the PSD. The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP 2000) [3] recommends that the results of patients who receive more than 2 Gy in a one-time procedure or 1 Gy in patients who tend to have a procedure multiple times should be recorded in their medical records. In our study, two patients (3.7%) had a PSD higher than 2 Gy and 20 patients (37%) had a PSD higher than 1 Gy which required monitoring according to the ICRP recommendation. For the stochastic effect according to the Radiation Protection Series Publication No. 8 [26], which was modified from the ICRP 1991 [1] and incorporates the risk terminology recommended by Calman [27], there are four groups at risk of cancer related to the effective dose. First is the effective dose <0.2 mSv, second is the effective dose Ōēź0.2 and <2 mSv, third is the effective dose Ōēź2 and Ōēż20 mSv, and the fourth is the effective dose >20 mSv. The first group has a minimal risk of cancer (~10-5 or less), the second group has a very low risk of cancer (~10-5 to 10-4), the third group has a low risk of cancer (~10-4 to 10-3), and the fourth group has a moderate risk of cancer (~10-3 or more). According to this research publication [26], the majority of patients (46 patients) in our study were in the moderate risk group for radiation-induced cancer. In fact, the incidence of cancer in the general population is about 25% (about one in four patients) [27,28]. When we calculated using the ICRP risk coefficient for fatal cancer [26], we found that the fatal cancer risk of patient radiation dose during the neurointerventional procedure at 20 mSv and 100 mSv were 250 times and 50 times lower than the cancer mortality rate in the general population, respectively. That is why the previous publications [28-30] concluded no clear risk of radiation-induced cancer at the low dose (<100 mSv). Therefore, in our opinion, the neurointerventional radiology procedures in this study were not considered moderate risk for radiation-induced cancer but were quite safe. Therefore, the first concern of the neurointerventional radiologists should be the benefit of the procedure for saving the life of the patients with cerebrovascular disease. However, the operators should also try to minimize the radiation dose if they can.
Many previous publications have reported on radiation doses in neurointerventional radiology procedures. A study by Persliden [7] used DAP to calculate the estimated skin dose which showed a little higher average calculated skin dose of about 1,250 compared to 1,009.68 in our study. Similar results were reported by Alexander et al. [6] who collected the radiation dose from both therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. The average dose of therapeutic procedures was about 2,292.3 mGy compared to 1,803 mGy in our study. The radiation doses in interventional radiology (RAD-IR) study reported by Miller et al. [19] also showed higher radiation doses than our study. In the RAD-IR study [19], the average skin dose of therapeutic neurointerventional procedures was about 2,106 mGy compared to 1,009.68 in our study. The RAD-IR study [19] published in 2003 presumably showed the highest radiation dose compared to the reports by Persliden [7] and Alexander et al. [6], published in 2005 and 2010, respectively. Our study period in 2015 was the latest report compared to the others. In the future, new techniques, more experience in neurointerventional radiology procedures, as well as better fluoroscopic machines may reduce the radiation dose. The individual skill of the operator is also involved in this perspective. However, most neuroradiological procedures are mandatory and are accepted to have more benefits in comparison to the minor risk from the radiation dose. Knowing the risks that may occur from the dose of radiation will bring more awareness in radiation protection and also follow-up of the patient to improve patient safety rather than not performing the neurointerventional radiology procedure.
There are some limitations of this study. First, we used the calculated PSD from the CD. Although a previous study [19] showed a good correlation between CD and PSD, it is still not the real PSD. Dose mapping or an instrument that can measure the actual skin dose would acquire more accurate parameters. Second, we also used the dose index to calculate the PSD from the CD. Actually, the dose index is operator- and procedure-specific, obtained by the measured real PSD. We used this parameter because we had no instrument to measure the real PSD; therefore, the accuracy of our PSD was reduced. Third, due to limited time and resources, we could collect data on only a small number of patients. However, the results may provide baseline data for our institution and the country. A longer study period or routine data collection in the future would be helpful to increase the number of patients. Last, this study focused only on radiation dose. We did not focus on other factors that cause high radiation dose. Further study is mandatory to find out what causes higher radiation dose in each procedure.
Not all neurointerventional radiology procedures are safe from deterministic complications. A small number of patients still received a dose higher than the threshold for skin complications and radiation-induced cataract. In terms of stochastic complications, we concluded that most neurointerventional radiology procedures in our study were at low risk of radiation-induced cancer compared with the risk in the general population.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Glenn K. Shingledecker of the International Affairs Office, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University for editing the English and also special thanks to Miss Nannapat Pruphetkeaw from the Epidemiology Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University for the statistical assistance.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Correlation of fluoroscopic time and CD at interventional referent point. CD, cumulative dose.
Table┬Ā1.
Demographic data
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| ŌĆāMale | 26 (48.1) |
| ŌĆāFemale | 28 (51.9) |
| Diagnosis | |
| ŌĆāAneurysm | 23 (42.6) |
| ŌĆāArteriovenous malformation | 23 (42.6) |
| ŌĆāDural arteriovenous fistula | 2 (3.7) |
| ŌĆāDural carotid carvernous fistula | 5 (9.3) |
| ŌĆāJuvenile angiofibroma | 1 (1.9) |
| Procedures | |
| ŌĆāGlue embolization | 25 (46.3) |
| ŌĆāCoiling* | 19 (35.2) |
| ŌĆāStent assisted coiling | 4 (7.4) |
| ŌĆāBalloon embolization | 3 (5.6) |
| ŌĆāCoil embolizationŌĆĀ | 2 (3.7) |
| ŌĆāPVA embolization | 1 (1.9) |
Table┬Ā2.
Overall radiation parameter
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| CD (mGy) | 1803 (654.5-4,130.4) |
| PSD (mGy) | 1,009.7 (366.5-2,313.0) |
| DAP (Gy-cm2) | 406.2 (156.4-874.8) |
| Effective dose (mSv) | 35.3 (13.6-76.0) |
| Fluoroscopic time (minutes) | 20.9 (4.3-60.4) |
Table┬Ā3.
Mean of dose and time analysis by procedures
| Procedure | CD (mGy) | DAP (Gy-cm2) | Fluoroscopic time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coiling* | 2,141 (718.3-4,130.7) | 409.4 (156.4ŌĆō835.2) | 23.7 (7.21-57.0) |
| Glu embolization | 1,519 (654.5-2,946.5) | 404.5 (183.0-874.8) | 15.9 (5.15-34.0) |
| Stent assisted coiling | 2,222.5 (946.7-3,691.3) | 428.9 (253.3-601.6) | 36.3 (27.6-44.6) |
| Balloon embolization | 1,281.6 (757.1-2,083.4) | 350.1 (239.8-550.4) | 10.1 (10.3-18.5) |
| Coil embolizationŌĆĀ | 1,828.3 (1,155.7-2,500.8) | 408.1 (270.4-545.8) | 41.2 (22.0-60.4) |
| PVA embolization | 1,295.1 | 462.9 | 22.4 |
Table┬Ā4.
Estimated PSD and effective dose
| Procedure | Effective dose | Estimate PSD |
|---|---|---|
| Coiling* | 35.6 (13.6-72.7) | 1,199.0 (402.3-2,313.2) |
| Glu embolizationŌĆĀ | 35.2 (15.9-76.1) | 850.6 (366.5-1,650.0) |
| Stent assisted coiling | 37.3 (22.0-52.3) | 1,244.6 (530.2-2,067.1) |
| Balloon embolization | 30.5 (20.9-47.9) | 717.7 (424.0-1,166.7) |
| Coil embolization | 35.5 (23.5-47.5) | 1,023.9 (647.2-1,400.5) |
| PVA embolization | 40.3 | 725.2 |
REFERENCES
1. ICRP. 1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 60. Ann ICRP 1991;21:1-3.

2. Wagner LK, Eifel PJ, Geise RA. Potential biological effects following high X-ray dose interventional procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1994;5:71-84.


3. ICRP. Avoidance of radiation injuries from medical interventional procedures. ICRP Publication 85. Ann ICRP 2000;30:7-67.

4. Berrington de Gonz├Īlez A, Darby S. Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries. Lancet 2004;363:345-351.


5. Bergeron P, Carrier R, Roy D, Blais N, Raymond J. Radiation doses to patients in neurointerventional procedures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1994;15:1809-1812.


6. Alexander MD, Oliff MC, Olorunsola OG, Brus-Ramer M, Nickoloff EL, Meyers PM. Patient radiation exposure during diagnostic and therapeutic interventional neuroradiology procedures. J Neurointerv Surg 2010;2:6-10.


7. Persliden J. Patient and staff doses in interventional X-ray procedures in Sweden. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 2005;114:150-157.


8. ICRP. Radiological protection in fluoroscopically guided procedures performed outside the imaging department. ICRP Publication 117. Ann ICRP 2010;40:1-102.

9. Tubiana M, Feinendegen LE, Yang C, Kaminski JM. The linear no-threshold relationship is inconsistent with radiation biologic and experimental data. Radiology 2009;251:13-22.



11. OŌĆÖDea TJ, Geise RA, Ritenour ER. The potential for radiation-induced skin damage in interventional neuroradiological procedures: a review of 522 cases using automated dosimetry. Med Phys 1999;26:2027-2033.


12. Balter S. Interventional fluoroscopy: physics, technology, safety, : New York, Wiley-Liss; 2001.
13. Vano E, Gonzalez L, Ten JI, Fernandez JM, Guibelalde E, Macaya C. Skin dose and dose-area product values for interventional cardiology procedures. Br J Radiol 2001;74:48-55.


14. van de Putte S, Verhaegen F, Taeymans Y, Thierens H. Correlation of patient skin doses in cardiac interventional radiology with dose-area product. Br J Radiol 2000;73:504-513.


15. Waite JC, Fitzgerald M. An assessment of methods for monitoring entrance surface dose in fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 2001;94:89-92.


16. McParland BJ. Entrance skin dose estimates derived from dose-area product measurements in interventional radiological procedures. Br J Radiol 1998;71:1288-1295.


17. Beir VII: health risks from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation. https://www.nap.edu/resource/11340/beir_vii_final.pdf. Accessed January 8, 2015
18. Tien HC, Tremblay LN, Rizoli SB, Gelberg J, Spencer F, Caldwell C, et al. Radiation exposure from diagnostic imaging in severely injured trauma patients. J Trauma 2007;62:151-156.


19. Miller DL, Balter S, Cole PE, Lu HT, Schueler BA, Geisinger M, et al. Radiation doses in interventional radiology procedures: the RAD-IR study: part I: overall measures of dose. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2003;14:711-727.


20. Wagner LK. You do not know what you are doing unless you know what you are doing. Radiology 2002;225:327-328.


21. International Electrotechnical Commission. Medical electrical equipment, part 2-43: particular requirements for the safety of X-ray equipment for interventional procedures, IEC; 2000,60601-2-43
22. Miller DL, Balter S, Noonan PT, Georgia JD. Minimizing radiation-induced skin injury in interventional radiology procedures. Radiology 2002;225:329-336.


23. Fletcher DW, Miller DL, Balter S, Taylor MA. Comparison of four techniques to estimate radiation dose to skin during angiographic and interventional radiology procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2002;13:391-397.


24. Schauer DA, Linton OW. National council on radiation protection and measurements report shows substantial medical exposure increase. Radiology 2009;253:293-296.


25. Sangkrut P, Boonkum K, Thamkitipan S, Suwanbundit A, Morwang W. Radiation dose to patient in interventional radiology. JIRTN 2007;1:51-60.
26. Radiation Protection Series Publication No. 8. Exposure of humans to ionizing radiation for research purposes, : Yallambie, Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency; 2005,pp 13-14.
28. Verdun FR, Bochud F, Gundinchet F, Aroua A, Schnyder P, Meuli R. Quality initiatives* radiation risk: what you should know to tell your patient. Radiographics 2008;28:1807-1816.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 12 Crossref
- 7,954 View
- 222 Download
- Related articles in NI
-
Anesthetic Consideration for Neurointerventional Procedures2014 September;9(2)
Recent Update of Guidelines for Neurointerventional Procedures2013 September;8(2)